As described, a regression line was fitted through 30 data points in the trees30.rda data set.
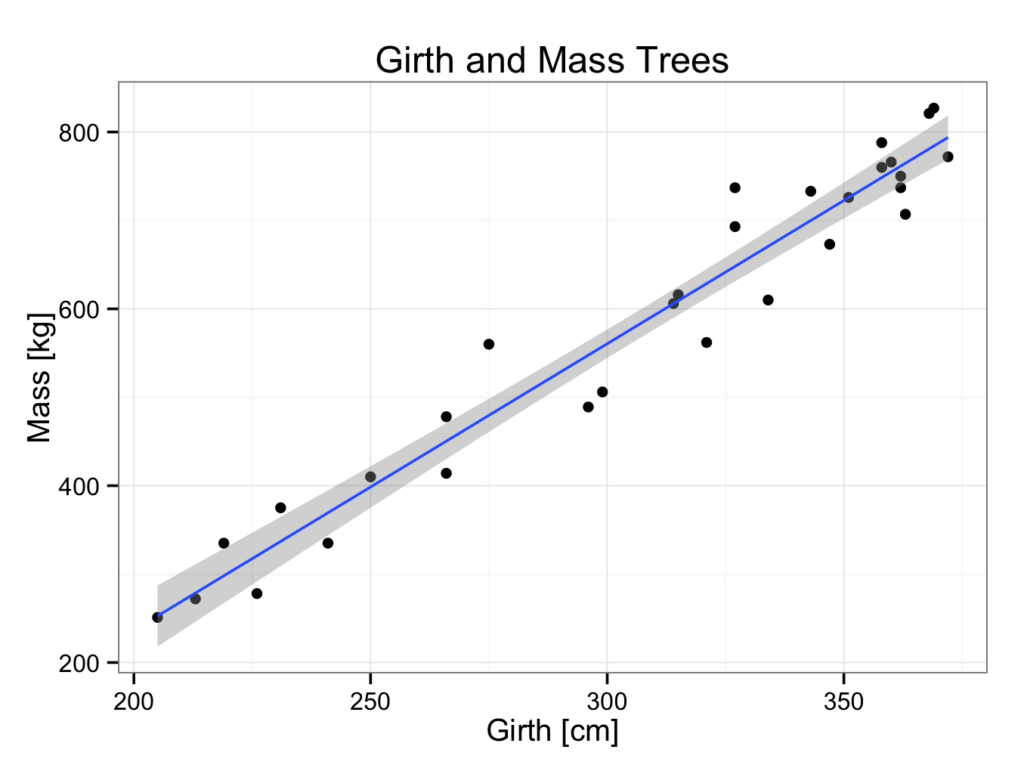
As can be seen in the graph, the line seems to fit the data well. However, the fit is not always as good as illustrated here. It would be nice to have a measure of how close the line fits the data. This measure is called the correlation coefficient and often denoted by R. It is defined as:
Obviously, computers are commonly used to calculate the correlation coefficient. In the tree example, the correlation coefficient can be found:
cor(TreeGirthMass$Girth,TreeGirthMass$Mass,method='pearson')
[1] 0.9731369
cor.test(TreeGirthMass$Girth,TreeGirthMass$Mass,method='pearson')
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: TreeGirthMass$Girth and TreeGirthMass$Mass
t = 22.366, df = 28, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
0.9437318 0.9872758
sample estimates:
cor
0.9731369 The correlation coefficient therefore is 0.9731 with a 95% confidence interval of (0.9437, 0.9873). The p-value for the test of no association is less than 0.001 (p<0.001) and significant. It is concluded there is an association between the girth and mass of the trees. How good this association is, is indicated by the correlation coefficient.
The correlation coefficient always has a value between –1 and 1. A correlation coefficient of 0.97 therefore, means that there is an excellent correlation between the girth and mass of a tree (it should be noted that the square of the correlation coefficient is always smaller than the correlation coefficient itself; this is because the square of a number between –1 and 1 is always smaller than the number itself).
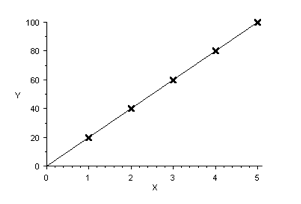
If the correlation coefficient = 1, the line fits the data perfectly:
A correlation coefficient of zero means that there is no correlation whatsoever:
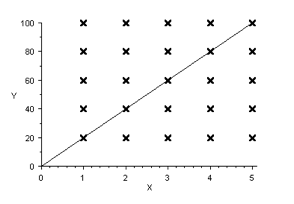
In fact, we could have drawn any line through the data points above! A correlation coefficient of –1, means that there is reverse relation between the data.
The correlation coefficient is a measure how close the line fits the data. It ranges from –1 to +1. A correlation coefficient of zero means that there is no correlation / association. The more the value approaches 1, the better the line fits the data. A negative value corresponds to a reverse relation.
Causation
Correlation may be demonstrated statistically. However, this does not necessarily demonstrate a cause (causation). Hill1 described the criteria for causation:
- strength
- consistency
- specificity
- temporality
- biological gradient
- plausibility
- experiment
- analogy